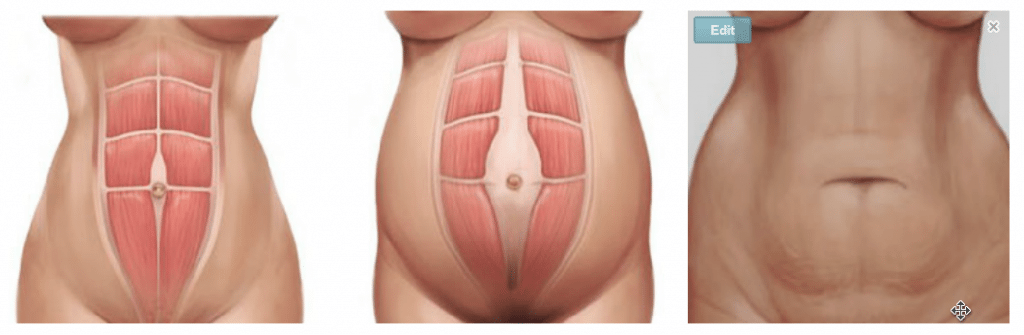
What Is Diastasis Rectus Abdominis?

The most common cause of DRA is pregnancy. As the fetus grows, the uterus expands and increases pressure against the stomach wall. This pressure causes the connective tissue to widen, increasing space between the right and left sides of the muscle. It may be noticed during or after pregnancy. Typically, DRA develops during the second or third trimester when the fetus grows most rapidly. DRA often resolves on its own during the first three months after the birth (postpartum). Other potential causes for DRA include:
- Frequent or rapid changes in weight.
- Stomach obesity.
- Genetics.
- Poor training technique or overloading the stomach wall during heavy lifting activities.
Infants commonly are born with a DRA that resolves over time without treatment. Pediatric doctors may monitor infants for the development of an umbilical hernia.
Several factors may make a person more prone to developing DRA. These include age, being pregnant with multiple children, and having had many pregnancies. The stomach muscles have many important functions within the body. These muscles aid in postural support, movement, breathing, and protection of the internal organs. For some people, a DRA may:
- Persist after pregnancy.
- Change the appearance of the stomach muscles.
- Result in reduced muscle strength.
For someone juggling the normal stresses of a new baby, discomfort, weakness, and changes to postural control, the added muscle weakness from a DRA may impact quality of life.
How Does It Feel?
Separated stomach muscles are usually painless and often have no symptoms. Some people, however, report problems that may be related to DRA that can include:
- Appearance.
- Discomfort.
- Difficulty doing certain activities.
A person with DRA may experience any of the following symptoms:
- A separation of the rectus abdominis muscle that is visible and felt by touching the stomach.
- Feelings of “flabbiness” in the stomach muscles.
- Low back, pelvic, or hip pain.
- Poor trunk posture.
- Feeling weak through the midsection.
- Doming or tenting of the middle of the stomach. This can occur during activities such as lifting, rolling over in bed, or certain exercises.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Your physical therapist will review your medical history and conduct a thorough interview. For women, this may include specific questions about:
- Pregnancies.
- Labor and delivery history.
- Type of delivery (cesarean or vaginal).
- Pain.
- Activities that make your symptoms better or worse.
- History of abdominal organ illness or surgeries.
- Types and level of physical demands at work, home, and sport.
Your physical therapist also will ask you when your symptoms began and how they impact your daily life.
They will gently feel your stomach muscle (palpate) to find if it has separated. Your physical therapist also will assess factors that can influence your strength, mobility, and endurance. These factors can include your:
- Posture.
- Breathing.
- Flexibility.
- Overall muscle strength.
- Movement patterns during certain activities.
How Can a Physical Therapist Help?
Physical therapy is a very effective way to manage the symptoms of DRA. It can improve your strength and stamina so you can return to normal activities. Your physical therapist may help you with:
Education. Your physical therapist can identify which movements or activities to modify or avoid as you recover. They will help you safely progress your activities as you heal. Your physical therapist will teach you safe and effective ways to regain your full function, so you can return to the activities that you enjoy.
Postural training. Learning to engage the deep core muscles through posture and breathing is one of the most important parts of treatment for people with DRA. This involves posture training and breathing to activate your deep core muscles as a unit. Postural training will focus on the:
- Transverse abdominis muscles.
- Diaphragm.
- Low back muscles.
- Pelvic floor muscles.
Your physical therapist will show you ways to do daily activities, such as lifting and carrying a baby or other objects. These methods will help to strengthen and reduce pressure on your stomach muscles
Exercise training. There are four layers of stomach muscles, and all are important in DRA rehabilitation. These muscles are the:
- Transverse abdominis.
- Internal and external obliques.
- Rectus abdominis.
A physical therapist can teach you the right type and intensity of exercises for your condition and goals. They can help you progress through them as you get stronger. Your physical therapist can address muscle imbalances. They also can show you stretches and diaphragm releases to help restore normal breathing patterns.
Bracing. Taping or braces for the abdominal region can provide support for some women with DRA during pregnancy. Your physical therapist also may recommend the use of support in the early phases of recovery. Support garments put the abdominal muscles in a more normal position. The tape or brace may remind you to safely use your core muscles during activities that increase pressure on the stomach. A brace or tape does not make your muscles weaker. Physical therapists treating pregnant women can make sure a support brace or garment is right for use during pregnancy.
Electrical muscle stimulation. This treatment may be used by a physical therapist to reduce DRA. It is used after pregnancy and in other adult populations. Electrical muscle stimulation gently activates the rectus abdominis muscle. It has been shown to improve function and reduce the amount of separation.
Can This Injury or Condition Be Prevented?
DRA is a natural consequence of pregnancy. In most cases it resolves on its own and does not impair function. Studies show that starting a program to stabilize the core and pelvic-floor muscles in early pregnancy is highly effective. It can improve function and help you manage the pressure that may worsen a DRA during and after pregnancy. A physical therapist can help women learn safe and effective exercise strategies to improve their:
- Pregnancy.
- Labor.
- Delivery.
- Experience after giving birth.
Physical therapy strategies to manage abdominal pressure during work activities and a personalized program of safe, progressive exercise also are effective for men and women with non-pregnancy-related DRA. If you develop DRA, the earlier you see a physical therapist, the faster you will be able to return to the activities you enjoy.